RAID is commonly used in enterprise environments, servers, network-attached storage (NAS) systems, and other data-intensive applications. It improves performance, data protection, and reliability by leveraging multiple physical drives’ combined power and redundancy.
What is Raid?
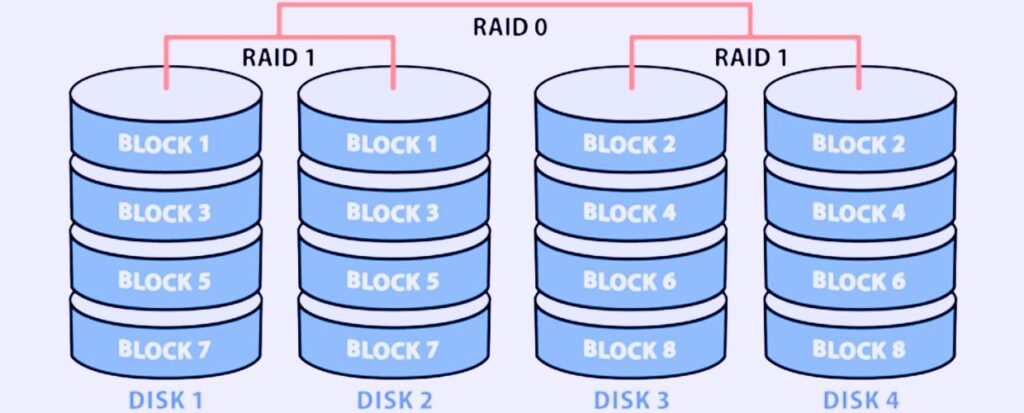
The Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) is a technology used to combine multiple physical hard drives into a single logical unit for data storage or to improve data performance and reliability. The solution provides enhanced storage capabilities by pooling together several drives and mitigates the risks associated with data loss and drive failures. There are several configurations, each with its characteristics and benefits. RAID 0, for instance, uses striping to split data across multiple drives, resulting in improved performance due to parallel data access. However, RAID 0 does not offer redundancy, meaning data loss can occur if one drive fails.
On the other hand, RAID 1 employs mirroring, where data is duplicated across two drives. While this configuration ensures data redundancy and allows for continued operation if one drive fails, it does not provide performance enhancements. Other levels, such as RAID 5, 6, and RAID 10, combine striping and parity information to provide varying degrees of performance and redundancy. These configurations offer fault tolerance, allowing data to be reconstructed even if one or more drives fail.
Why is Raid important?
The storage solution is an important technology in data storage and management. It offers numerous benefits and enhances data performance, reliability, and security. Some of the important are given below:
Data Redundancy and Fault Tolerance
One of the primary purposes of the storage technique is to provide data redundancy and fault tolerance. By distributing data across multiple drives and utilizing parity information, RAID configurations allow data recovery in case of drive failures. This redundancy ensures that even if one or more drives fail, the system can continue to operate, and data remains accessible. It is crucial in environments where uninterrupted access to data is essential, such as servers and enterprise systems.
Improved Data Performance
It can significantly enhance data performance by leveraging the combined power of multiple drives. In configurations like RAID 0 and RAID 10, data is striped across multiple drives, enabling simultaneous read and write operations. This parallelism results in faster data transfer rates and improved overall system performance, making it ideal for applications requiring high-speed data access, such as multimedia editing or database servers.
Scalability and Capacity Expansion
The storage solution expands storage capacity by adding more drives to the array. With the technique, it is possible to seamlessly integrate additional drives without disrupting the existing data or applications. This scalability is particularly beneficial in scenarios where storage requirements grow over time, providing flexibility and the ability to adapt to changing needs.
Improved Data Access and Availability
The configurations, such as RAID 1 or 10, provide faster data access and improved availability. With mirrored drives, data can be simultaneously read from multiple drives, resulting in faster retrieval times. Additionally, in case of a drive failure, the system can automatically switch to a redundant drive, ensuring continuous access to data and minimizing interruptions.
Application of Raid
The storage technique finds wide application in various industries and environments where data storage, performance, and reliability are critical. Some of the applications are given below:
Enterprise Servers
It is extensively used in enterprise-level servers to ensure high-performance data storage and fault tolerance. To support critical applications and services, servers require fast access, redundancy, and continuous operation. The configurations like RAID 5 or RAID 6 balance performance and redundancy, allowing seamless operation even during drive failures.
Network-Attached Storage (NAS)
NAS devices are used to centralize and share data across a network. It is commonly employed in NAS systems to provide fault tolerance and high storage capacity. By implementing the storage array, NAS devices can offer redundancy, ensuring data remains accessible even if a drive fails. It is particularly important in shared storage environments where data availability is crucial.
Multimedia Editing and Production
Its high-performance capabilities make it ideal for multimedia editing and production workflows. Tasks like editing, animation, or rendering require rapid access to large multimedia files. The configurations such as RAID 0 or RAID 10 allow for simultaneous data access across multiple drives, significantly improving the read and write speeds, thereby reducing processing times and enhancing productivity.
Database Servers
Databases are the backbone of many applications and systems, and their performance is critical for efficient data processing. The technology, particularly RAID 10, is commonly used in database servers to ensure performance and redundancy. RAID 10 provides striping and mirroring, enabling high-speed data access while maintaining redundancy. It improves database responsiveness and safeguards against potential data loss.
Benefits of Raid
The storage solution offers numerous benefits regarding data storage, performance, and reliability. Some of the benefits are given below:
Enhanced Data Protection
It provides an additional layer of data protection beyond regular backup solutions. By distributing data across multiple drives and implementing redundancy, RAID mitigates the risk of data loss due to drive failures. In a drive failure, data can be rebuilt or retrieved from the remaining drives, ensuring data integrity and minimizing the impact on business operations.
Increased Uptime and Availability
RAID 1 or 10 configurations offer increased uptime and data availability. Mirrored drives in RAID 1 maintain an identical copy of data on separate drives, allowing immediate access even if one drive fails. Similarly, RAID 10 combines striping and mirroring, providing performance benefits and redundancy. These configurations reduce the downtime associated with drive failures, ensuring continuous operation and uninterrupted access to critical data.
Efficient Space Utilization
The technique optimizes disk space utilization, providing efficient storage management. Parity information is distributed across the drives in configurations like RAID 5 or RAID 6, reducing the overall storage overhead. It means that a portion of the total capacity is used for redundancy while maximizing usable space. Its efficient space utilization is particularly advantageous in environments where storage capacity needs to be maximized while maintaining data protection.
Cost-Effectiveness
The technology offers a cost-effective solution for data storage and protection. By combining multiple drives into a storage array, organizations can achieve higher performance and data redundancy without needing expensive individual high-capacity drives. It enables organizations to maximize the utilization of existing drives, providing an efficient and cost-effective storage solution.
Limitation of Raid
While the technology offers numerous benefits, its limitations must be considered. Let’s explore some of the key limitations.
Cost
Implementing the storage system can involve additional costs. Depending on the level and configuration, organizations may require to invest in additional hard drives, controllers, or specialized hardware. The systems with higher redundancy or performance enhancements can be more expensive, so weigh the benefits against the associated costs.
Complexity
The configurations can be difficult to set up and manage, especially for non-technical users. Configuring and maintaining storage arrays often require specialized knowledge and expertise. Incorrect configuration or management errors can lead to data loss or reduced performance. Proper planning, implementation, and ongoing monitoring are necessary to ensure optimal performance and data integrity.
Capacity and Overhead
Certain configurations, such as RAID 1 or 10, provide data redundancy through mirroring, duplicating data across multiple drives. While this offers high fault tolerance, it also reduces the effective storage capacity. For example, in a RAID 1 configuration with two drives, the usable capacity is limited to the size of a single drive. Additionally, the implementations require some overhead for parity information or redundancy, reducing the available storage capacity.
Performance Impact in Certain Configurations
While the storage solution can enhance performance, not all configurations guarantee performance improvements in all scenarios. RAID 1 and RAID 10 configurations provide redundancy but may not offer significant performance enhancements compared to other levels. RAID 5, which distributes parity information across drives, can experience reduced write performance due to the need to calculate and update parity data.
Conclusion
RAID technology offers significant data storage, performance, and reliability benefits. It provides data redundancy, fault tolerance, improved performance, scalability, enhanced data protection, increased uptime, efficient space utilization, improved data integrity, and cost-effectiveness. It is widely applied in various industries and environments, including enterprise servers, network-attached storage (NAS), multimedia editing, database servers, video surveillance systems, data centers, virtualized environments, and small business setups.
The storage technique offers a robust data storage and management solution, balancing performance and redundancy. By leveraging the benefits of RAID technology, organizations can enhance their data infrastructure, protect against data loss, improve system performance, and ensure uninterrupted access to critical data.
Read the Latest Technology and Business News:
TechGolly Latest News
TechGolly Future Tech News
TechGolly Business News
TechGolly Product News
TechGolly Stock Market News
TechGolly Research News


